How to Find My MAC Address: A Simple Guide to Networking
Understanding how to find your MAC address is crucial for effective network management and security. The MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications at the data link layer of a network segment. This guide will walk you through various methods to locate your MAC address on different devices, including Windows, Mac, Linux, and mobile platforms.
Find MAC Address on Windows
Finding your MAC address on Windows is a straightforward process that can be done through the Settings app or the Command Prompt. The MAC address is essential for identifying network hardware, ensuring secure connections, and optimizing network performance. To find MAC address on Windows, follow these steps:
Using Settings
1. Open the Settings app by clicking on the Start menu and selecting the gear icon.
2. Navigate to Network & Internet.
3. Depending on whether you’re using a wired connection or Wi-Fi, select Status or Wi-Fi from the sidebar.
4. Click on Hardware properties.
5. You will see your MAC address listed under Properties, labeled as Physical Address (MAC).
Using Command Prompt
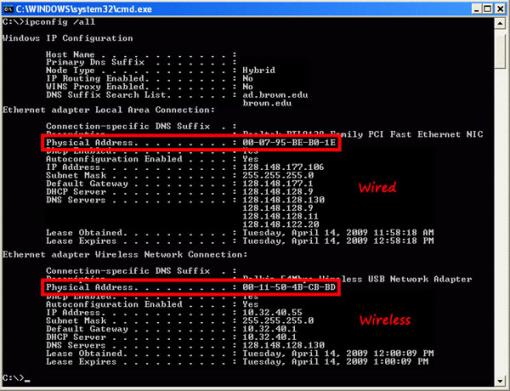
To use the Command Prompt to locate your MAC address, follow these steps:
1. Press Win + R to open the Run dialog.
2. Type cmd and hit Enter.
3. Type getmac and press Enter.
4. Your MAC address will be displayed in the results. It may look like this: 00:14:22:01:23:45.
Locate MAC Address on Mac
On a Mac, you can easily check MAC address in system preferences or leverage the Terminal. This identifier is vital for connecting your Mac securely to various networks, including wired and wireless. Here’s how:
Using System Preferences
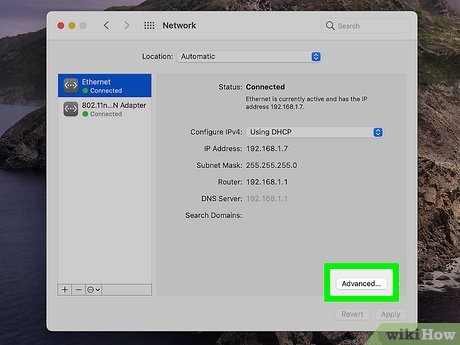
1. Click on the Apple logo in the top-left corner and select System Preferences.
2. Choose Network.
3. Select your active network connection (Wi-Fi or Ethernet) from the left side.
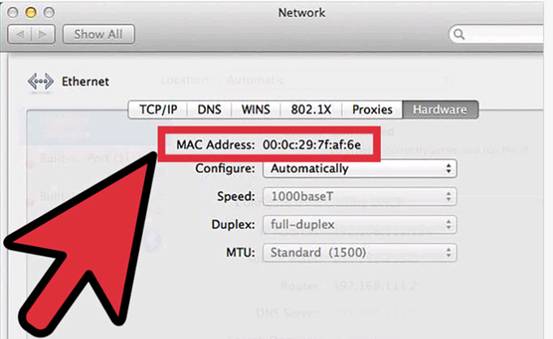
4. Click on Advanced, then choose the Hardware tab.
5. Your MAC address will be visible here, formatted as six pairs of hexadecimal digits (e.g., 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E).
Using Terminal
Alternatively, you can use the Terminal app:
1. Open Terminal from your Applications or Spotlight.
2. Type ifconfig and hit Enter.
3. Look for your active network interface (usually en0 for Wi-Fi) and find the line that starts with ether; that’s your MAC address.
Check MAC Address in Linux
To find a MAC address on Linux, you have several command-line utilities at your disposal. Knowing your device’s MAC address can help with network troubleshooting and configurations.
Using Terminal Commands
1. Open a Terminal window.
2. Type ip link and press Enter. This command will list network interfaces along with their MAC addresses.
3. You can also use ifconfig if it’s installed, and look for the corresponding MAC address next to ether for your active interface.
Finding MAC Address through Network Settings
If your Linux distribution has a settings GUI (such as Ubuntu):
1. Go to Settings > Network.
2. Select your active network interface.
3. Your MAC address will usually be listed under the connection details or properties.
Find MAC Address on Router
Accessing your router’s settings is another method to find MAC address on router. Each connected device’s MAC address can often be found in the routers’ DHCP client list or connected devices section, which aids in identifying network anomalies.
Accessing Router Settings
1. Open a web browser and type your router’s IP address (usually 192.168.0.1 or 192.168.1.1).
2. Log in with your admin credentials.
3. Navigate to the Device List, DHCP Clients, or a similar section in your router’s dashboard.
4. Each connected device, along with its MAC address, should be displayed here.
Using a MAC Address Finder Tool
Utilizing third-party MAC address finder tools can also simplify this process. These tools can scan your network and compile a list of connected devices along with their MAC addresses, enhancing the visibility of network devices.
View MAC Address on Smartphones
Accessing your MAC address on smartphones involves different steps depending on the operating system. This is crucial for establishing secure connections to networks while using mobile devices.
Find My MAC Address on iPhone
1. Open the Settings app.
2. Tap on General > About.
3. Scroll down to find Wi-Fi Address, which is your MAC address for Wi-Fi, formatted as six pairs of characters (e.g., 00:1A:2B:3C:4D:5E).
Detect MAC Address on Android
For Android devices, steps vary slightly:
1. Open Settings.
2. Navigate to About Phone > Status.
3. Look for the Wi-Fi MAC address. This is the unique identifier for your Android device’s Wi-Fi interface.
Key Takeaways
- Finding your MAC address is essential for network connectivity and security.
- Different devices (Windows, Mac, Linux, mobile) require specific methods to view MAC addresses.
- Accessing your router helps to see all connected devices’ MAC addresses.
FAQ
1. Why do I need to find my MAC address?
Finding your MAC address is important for network configuration, security, and troubleshooting connectivity issues. It helps identify your device on shared networks and ensure that MAC addresses are correctly assigned for network access.
2. Can I change my MAC address?
Yes, changing your MAC address, also known as MAC address spoofing, can help enhance privacy or troubleshoot network issues. However, it requires appropriate permissions, and it may affect your network access.
3. What is the difference between an IP address and a MAC address?
An IP address is used for identifying devices in a network based on their location, while a MAC address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface for communications at the data link layer. Both are essential for networking, serving separate roles.
4. How often do I need to check my MAC address?
You typically do not need to check your MAC address often. However, you should check it when troubleshooting network issues, connecting to secure networks, or when devices are not communicating as expected.
5. Are there risks associated with changing my MAC address?
Yes, changing your MAC address can lead to issues such as losing network connections, especially if the new address conflicts with other devices on the network. It may also affect network policies that rely on MAC filtering.
Images: