How to Properly Enable Virtualization in BIOS
Understanding how to enable virtualization is crucial for optimizing your computer’s performance, especially if you are looking to run virtual machines for development, testing, or normal usage. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the necessary steps to enable virtualization in BIOS in 2025. We’ll cover access methods, settings for virtualization in BIOS, and answers to common questions, ensuring a thorough understanding of the process.
Accessing BIOS Setup
The first step to enabling virtualization in BIOS is to **access the BIOS setup**. Each motherboard manufacturer has a different method to access BIOS, so you should refer to your system’s documentation. Generally, you can enter the BIOS during the boot-up process by pressing a specific key, often F2, Del, or Esc. To provide a clearer understanding:
Method to Enter BIOS
To **access BIOS setup**, restart your computer and look for a prompt on the screen that indicates which key to press. This usually appears for a few seconds when your computer is turning on. If you’re unsure, check your motherboard or system manual for exact instructions. Once you press the correct key, you will enter the BIOS setup utility, where you can configure **virtualization settings in BIOS**.
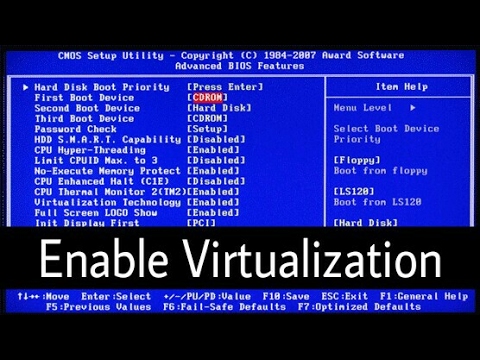
Navigating BIOS Menu Options
Utilize your keyboard arrows to navigate through the **BIOS menu options**. Look for sections named “Advanced,” “CPU Configuration,” or “Chipset.” Different BIOS versions might vary in organization, so it may take some time to familiarize yourself with the layout. Always proceed with caution to avoid unintentional changes that could affect your system’s settings.
Saving Changes and Exiting
Once you’ve accessed the required settings, make sure to save any changes and exit the BIOS setup. Typically, you can do this by pressing F10 and selecting “Yes” to confirm changes. After exiting BIOS, your system will reboot, applying any modifications.
Enabling Virtualization Technology
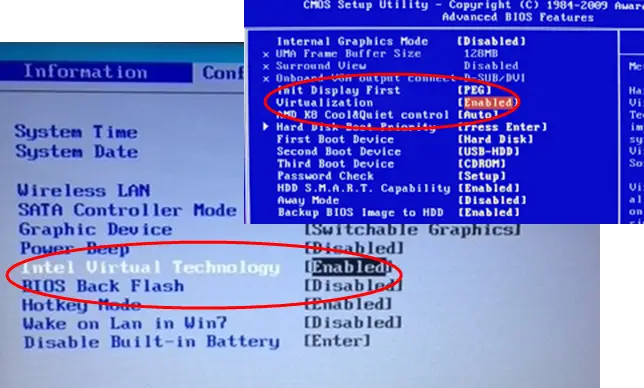
Now that you have accessed the BIOS setup, the next step involves enabling the virtualization features which might be labeled as **“Intel Virtualization Technology”, “AMD Virtualization”, or simply “VT-x” or “AMD-V”**. Locating these options is essential for achieving effective virtualization.
Finding the Virtualization Option in BIOS
In the BIOS settings, navigate to the appropriate section, often listed under “Advanced” or “CPU Configuration.” Here, look for terms like “Virtualization Technology,” “Vanderpool,” or “SVM Mode” (for AMD systems). To **turn on virtualization**, ensure the setting is enabled. For example, enabling **Intel Virtualization Technology** or adjusting **AMD V** settings allows Windows or Linux to use virtualization capabilities more effectively.
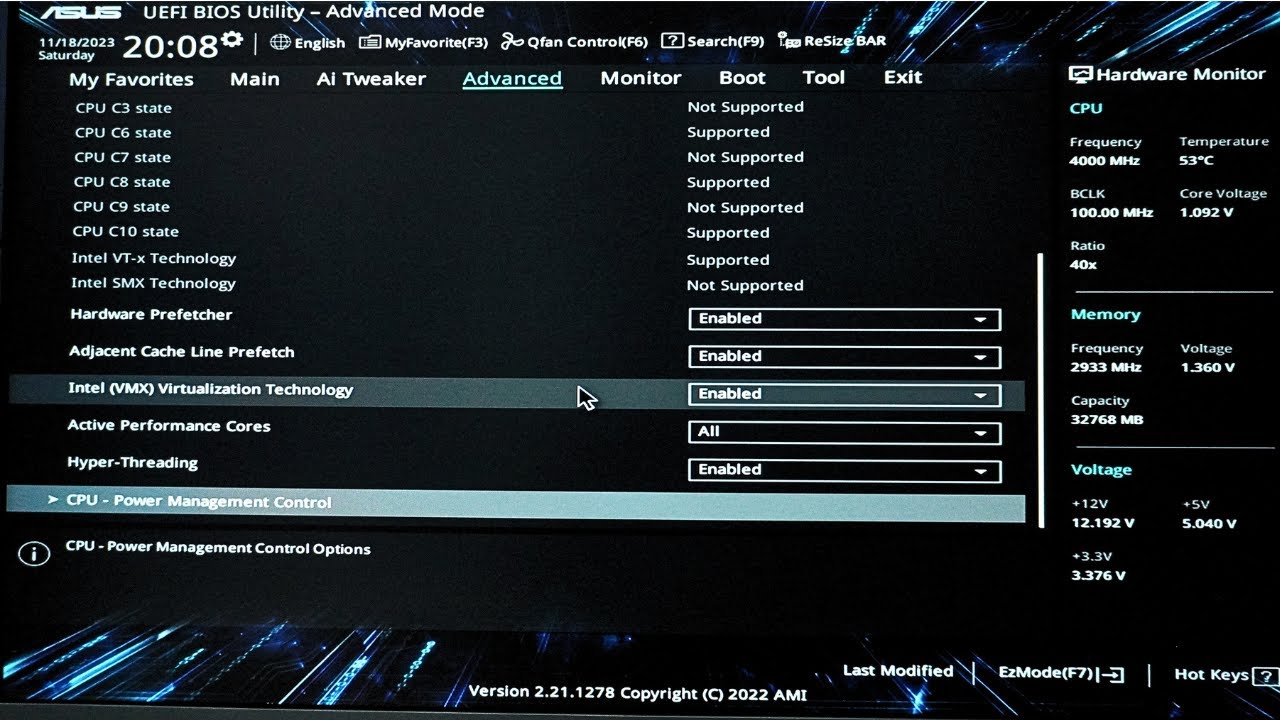
Enable Hyper-V Virtualization Support
If you are on a Windows system and require **Hyper-V virtualization support**, upon enabling **Intel/AMD virtualization**, look for an option labeled “Hypervisor Support” and set it to enabled. Doing so enhances your virtualization environment, allowing optimized performance for any virtual machines that you may run.
Checking Virtualization Support
After adjusting the BIOS settings, it’s wise to double-check that the changes have taken effect. You can do this in several ways: install a virtualization software like VMware or VirtualBox and look for indicators that confirm whether the virtualization capabilities are enabled. Additionally, running a CPU check tool can quickly verify if **virtualization support is effective**. This helps ensure no steps were overlooked.
Configuring Additional Virtualization Settings
Following the basic enablement of virtualization, further configurations may be required depending on your intended applications. Configuring settings in the BIOS that directly relate to virtualization can improve performance significantly.
Customize Virtual Machine Settings in BIOS
If your BIOS includes options for customizing **virtual machine settings** or allocation of system resources such as CPU cores and memory, take advantage of these settings. Adjusting parameters like total memory for virtual machines helps manage system overload during heavy multitasking. This can lead to smoother operation of virtual environments, much required for developers or for running test environments.
Understanding Virtualization Features
Insights into **virtualization features in BIOS**, such as VT-d or IOMMU for device isolation and failure contexts, can aid users in optimizing their virtual machines for specific workloads. Make sure they are enabled if you need advanced features for server deployments or enhanced performance in environments requiring ruggedness.
BIOS Updates for Virtualization
Lastly, keeping your BIOS firmware updated ensures compatibility with the latest virtualization technologies. Newer updates may unlock features that were previously unavailable or unstable in older versions. Regularly check your motherboard manufacturer’s website for updates, and apply them as needed before delving into virtualization configuration, smoothing out any potential hiccups in the enabling process.
Key Takeaways
- Accessing BIOS requires pressing specific keys during boot-up.
- Enabling **virtualization features** involves finding the right settings based on your CPU type.
- Post-configuration, verifying settings will decrease troubleshooting in the future.
- Regular updates of BIOS firmware enhance virtualization tools and compatibility.
- Customizing virtualization performance through BIOS can significantly improve efficiency.
FAQ
1. How do I know if virtualization is enabled?
You can check if virtualization is enabled by going into Task Manager (Windows) or using terminal commands in Linux. In Task Manager, under the Performance tab, you should see “Virtualization: Enabled” when viewing processes if virtualization is configured properly.
2. What specific settings should I look for in BIOS for AMD systems?
In AMD systems, look for “SVM Mode” to enable AMD virtualization. Ensuring this option is enabled is critical for allowing the use of tools like Hyper-V or VMware effectively.
3. Can BIOS virtualization settings affect my system’s performance?
Yes, improperly configured virtualization settings can impact system performance, particularly under high load. Effective adjustments in your BIOS can improve resource allocation for running virtualization software efficiently.
4. Is it safe to enable virtualization?
Enabling virtualization in BIOS is generally safe and necessary if you need to run virtual machines. However, ensure your hardware supports it and all drivers are up-to-date. This avoids compatibility issues in your operating system.
5. What if my BIOS does not provide virtualization options?
If your BIOS does not present any virtualization options, check your CPU specifications to ensure it supports virtualization technology. You may also need a BIOS update or refer to your motherboard’s manual for guidance.
6. Will enabling virtualization void my warranty?
No, enabling virtualization typically does not void the warranty; however, adjusting other system settings outside standard use might. Always consult your user manual or manufacturer for warranty details regarding BIOS modifications.